Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service
Exosomal proteomic detection is a high-throughput analytical technique focused on profiling the proteome of exosomes. Exosomes are nanoscale vesicles secreted by cells, widely found in bodily fluids, carrying proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and other molecules that mediate intercellular communication. Using high-resolution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and other techniques, this service enables comprehensive analysis of exosomal proteins, including their composition, post-translational modifications (PTMs), and abundance variations.
Exosomal proteomic detection service is widely applied in fields such as cancer diagnosis, neurodegenerative disease research, immune regulation, drug development, and precision medicine. For example, in cancer research, the service can help identify tumor markers present in exosomes; in neurodegenerative disease studies, it can reveal disease-associated exosomal protein changes; and in immunology, it can explore the role of exosomes in modulating immune responses. These applications provide robust data support for biomarker discovery, new drug development, and disease mechanism investigations.
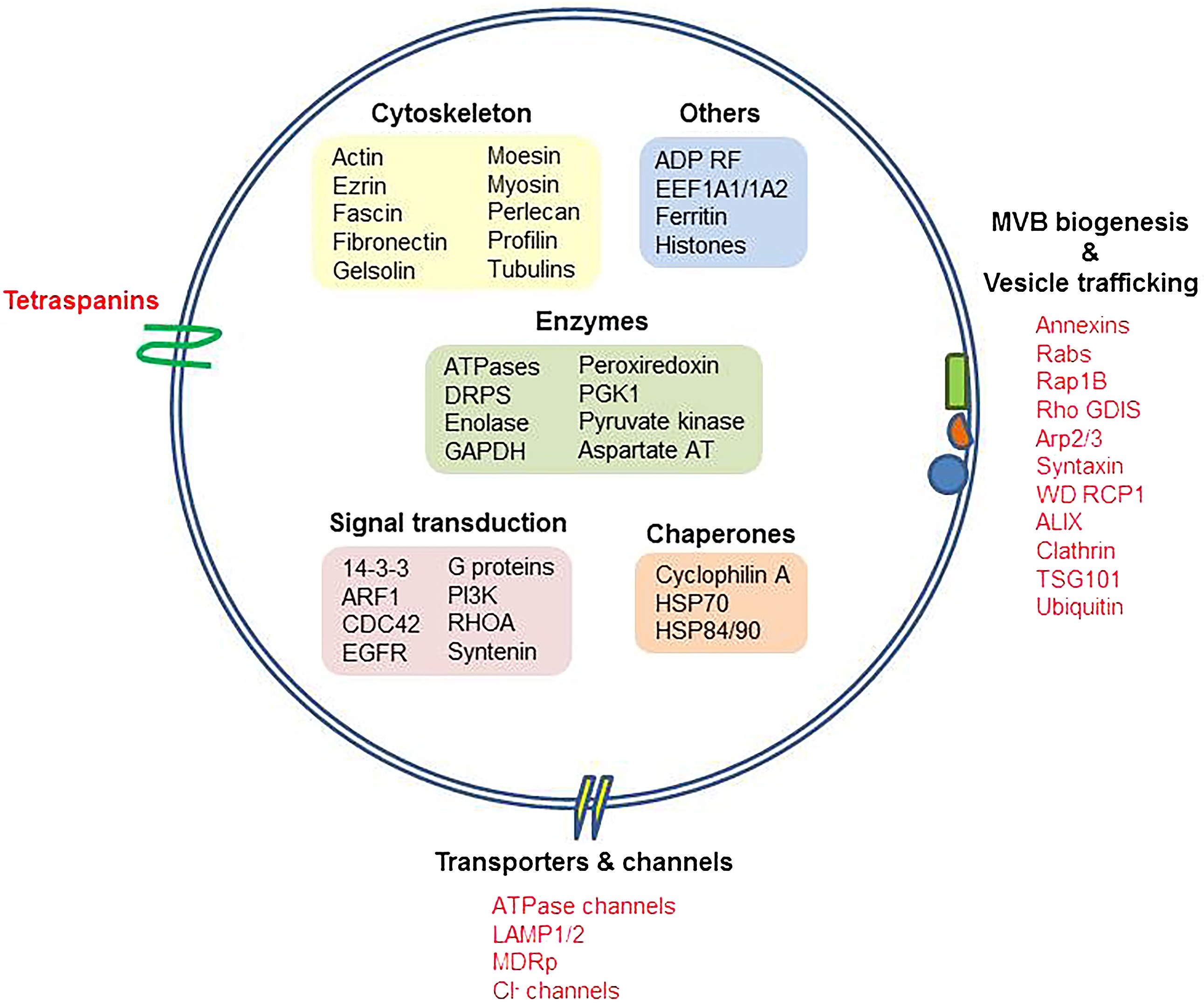
Siles-Lucas, M. et al. Veterinary Parasitology, 2017.
Figure 1. Exosome Signatures and Exosomal Proteins.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on a high-resolution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) platform and incorporating advanced sample preparation and enrichment strategies, MtoZ Biolabs’ exosomal proteomic detection service enables comprehensive analysis of exosomal proteins. By isolating exosomes from blood, urine, cell culture supernatants, and other sample types, then conducting efficient protein extraction and separation, this service ensures high-sensitivity, high-resolution identification and quantification of exosomal proteins. It provides detailed insights into protein composition, abundance variations, and post-translational modifications, assisting researchers in exploring the potential applications of exosomes in disease diagnosis, therapeutic monitoring, and biomarker discovery.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Exosomes are isolated from cell culture supernatant, plasma, or other biological fluids, ensuring high-purity and high-quality samples.
2. Exosome Characterization
Exosomes are characterized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and Western blot validation to confirm morphology, size, and specific markers.
3. Protein Extraction and Digestion
Total protein is extracted from the isolated exosomes and digested into peptides, preparing them for subsequent mass spectrometry analysis.
4. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
High-resolution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) is employed for high-throughput identification and quantification of exosomal proteins.
5. Data Analysis
Specialized bioinformatics software is used to process the mass spectrometry data, including protein identification, quantification, functional annotation, and pathway enrichment analysis, revealing the biological significance of exosomal proteins.
6. Results Report
A comprehensive analysis report is provided, containing the identified protein list, quantitative results, functional enrichment analysis, and relevant figures, supporting subsequent research and applications.
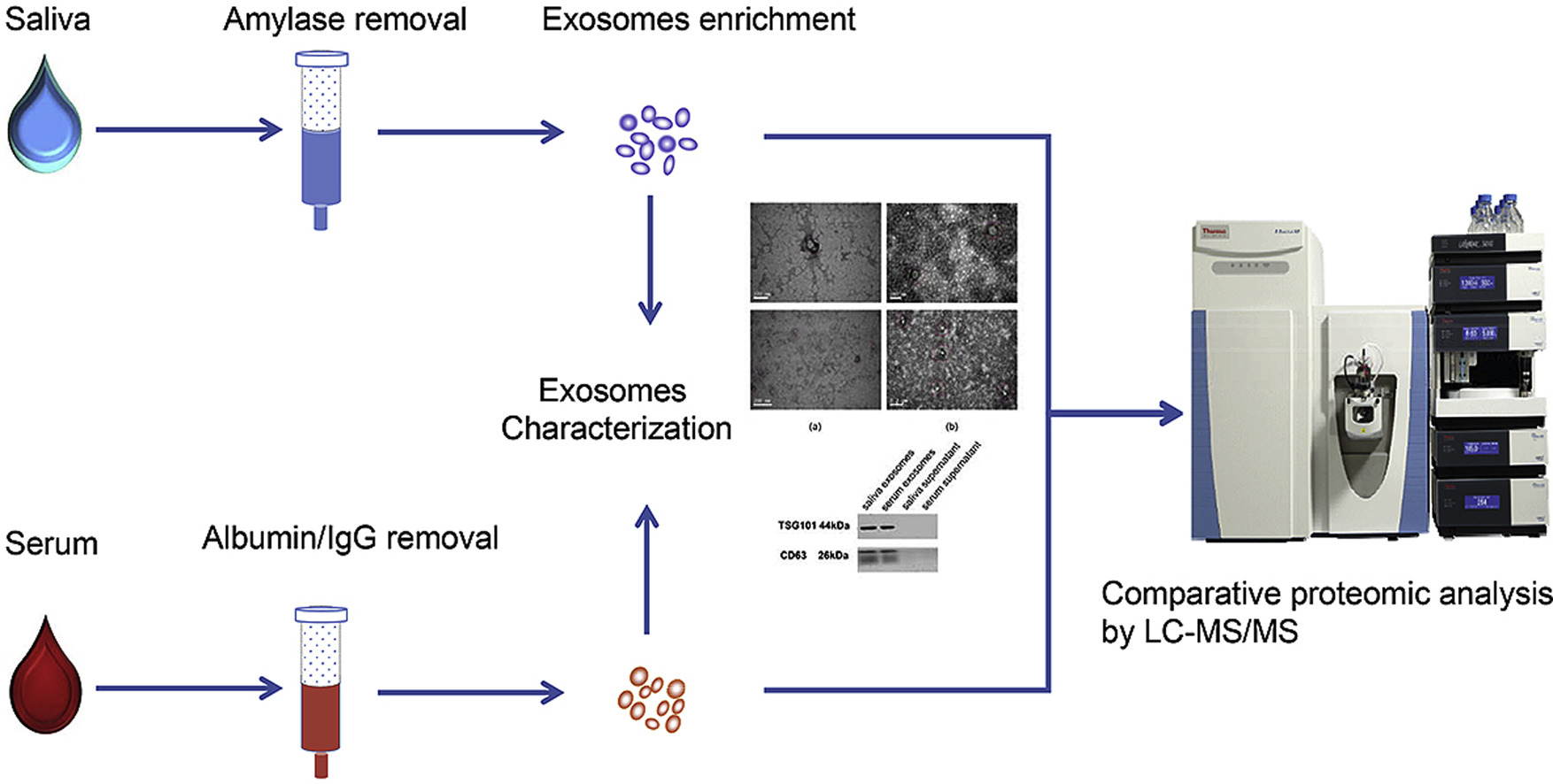
Sun, Y. et al. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2017.
Figure 2. Saliva and Serum Exosome Proteomics Workflow.
Service Advantages
1. High Sensitivity
Utilizing high-resolution mass spectrometry technology, exosomal proteins can be efficiently extracted and analyzed from complex samples, ensuring high sensitivity in detection and accurate protein identification.
2. Comprehensive Profiling
Combining advanced exosome enrichment techniques with efficient mass spectrometry analysis enables a thorough investigation of exosomal proteomes, revealing their dynamic changes under various physiological and pathological conditions.
3. Quantitative Analysis
Through high-throughput and precise quantification methods, the service provides relative abundance data of exosomal proteins, supporting subsequent functional research and biomarker discovery.
4. Flexible Customization
Tailored experimental designs and data analysis solutions are offered based on specific research needs, ensuring that study outcomes closely align with research objectives.
Applications
1. Cancer Research
Exosomal proteomic detection service can analyze tumor patients to identify potential cancer biomarkers, aiding early diagnosis, monitoring disease progression, and assessing treatment response.
2. Immune Disease Research
In autoimmune disease and immunotherapy studies, exosomes serve as vital carriers for intercellular signaling. Analyzing their proteomes helps shed light on immune response mechanisms.
3. Neurodegenerative Diseases
The dynamic changes in exosomal proteins reflect the pathological progression of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, offering new diagnostic and therapeutic targets.
4. Drug Development
Exosomal proteomic detection service can evaluate the effects of drugs on cellular functions, aiding in the screening of potential drug targets and efficacy assessment.
Case Study
1. Exosomal Proteomics and Cytokine Analysis Distinguish Silicosis Cases from Controls
The study aimed to distinguish silicosis patients from healthy controls through exosomal proteomics and cytokine analysis, with the goal of identifying potential biomarkers and exploring the pathogenic mechanisms of silicosis. The study involved miners diagnosed with silicosis and a control group of healthy individuals. High-resolution mass spectrometry was used to comprehensively profile plasma exosomal proteins, and various cytokine detection techniques were employed to systematically analyze differences between the groups. The results revealed significant changes in the exosomal protein profiles of silicosis patients compared to controls. Several inflammation-related proteins were upregulated, and certain cytokines exhibited markedly elevated expression levels. Functional analysis indicated that these differential proteins and cytokines were closely associated with inflammatory responses, immune regulation, and pulmonary fibrosis, suggesting that they may be key pathological factors in silicosis. The findings concluded that exosomal proteins and cytokines could serve as biomarkers to differentiate silicosis patients from healthy controls, uncovering molecular pathways associated with disease progression and providing new directions for early diagnosis and therapeutic interventions.
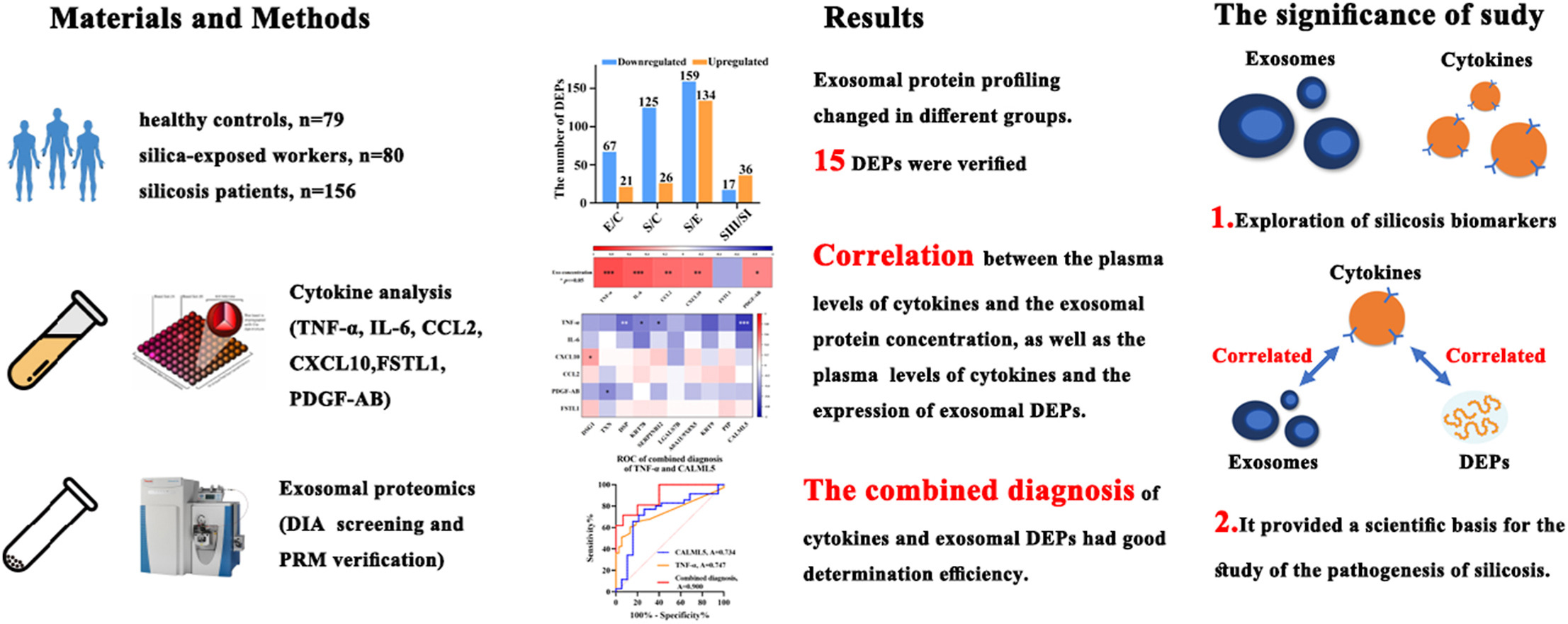
Yao, J H. et al. Environmental Pollution, 2024.
Figure 2. The Graphical Abstract of the Study.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Relevant Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Parameters
4. The Detailed Information of Exosome Proteomics Identification
5. Mass Spectrometry Image
6. Raw Data
How to order?







