Exosomal Cytokines Profiling Service
Exosomal Cytokines Profiling Service enables the detection of the types, expression levels, and changes of cytokines within exosomes, helping to reveal the molecular mechanisms of diseases, diagnostic biomarkers, and potential therapeutic targets. Cytokines are low-molecular-weight proteins or peptides secreted by immune cells (such as T cells, B cells, macrophages) and certain non-immune cells (such as endothelial cells and fibroblasts). They are primarily responsible for cell-to-cell signaling. Cytokines interact with specific receptors on target cells to regulate immune responses, inflammation, cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Exosomal Cytokines refer to the cytokines that are either encapsulated inside exosomes or bound to the exosomal membrane. Compared to free-floating cytokines in bodily fluids, cytokines carried by exosomes are more stable and can selectively be transferred to target cells, influencing cellular functions. Common techniques used for Exosomal Cytokines Profiling include multiplex immunoassays, flow cytometry, mass spectrometry, ELISA, and others. MtoZ Biolabs offers Exosomal Cytokines Profiling Service utilizing one or more techniques based on specific research needs to analyze exosomal cytokines, providing support for understanding the distribution of cytokines within exosomes and their relationship with diseases.
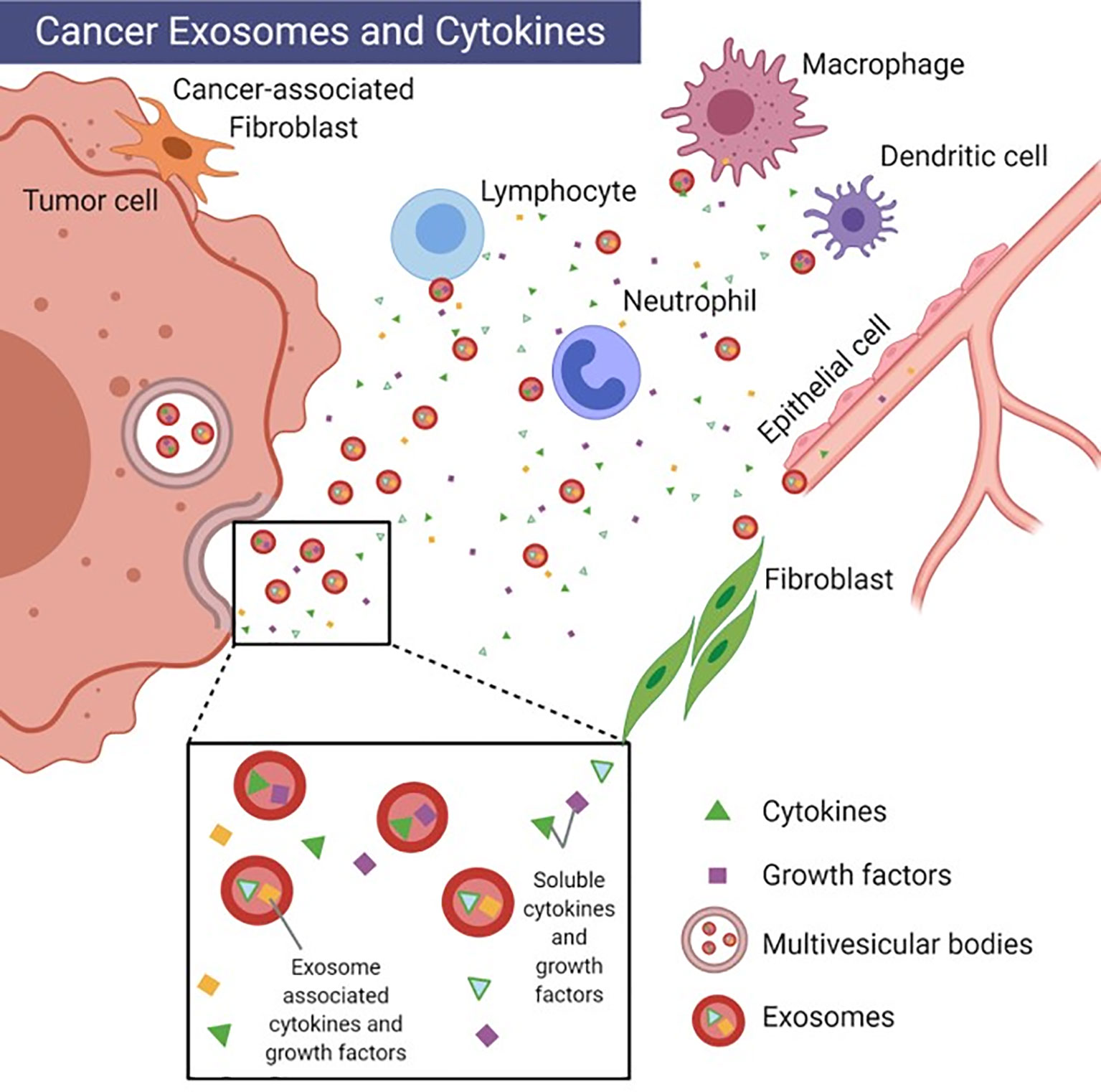
Benjamin-Davalos S. et al. Frontiers in immunology. 2021.
Analysis Workflow
The main steps of Exosomal Cytokines Profiling Service are as follows:
1. Exosome Extraction
Exosomes are extracted from bodily fluids using ultracentrifugation or other exosome separation techniques.
2. Exosomal Cytokine Extraction
Cytokines are extracted using techniques such as immunoaffinity capture.
3. Cytokine Analysis
Appropriate techniques (such as multiplex immunoassays, flow cytometry, or mass spectrometry) are selected based on experimental needs to analyze the cytokines.
4. Data Analysis
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the cytokines is performed.
Applications
Examples of Exosomal Cytokines Profiling Service applications:
Inflammation and Immune Response Monitoring
Exosomal Cytokines Profiling can be used to identify biomarkers associated with immune diseases, allergic reactions, and autoimmune disorders.
Cancer Immune Monitoring
By analyzing the levels of cytokines in exosomes from tumor patients, the immune evasion mechanisms can be assessed, patient prognosis can be predicted, and new immunotherapy strategies can be developed.
Infectious Disease Research
By analyzing the expression of various cytokines (such as IFN-γ, IL-12, etc.) in exosomes, the host immune response during infection can be revealed.
Drug Evaluation
Cytokine analysis in exosomes can assess the impact of drug treatments on the immune system, especially in immunotherapy and targeted therapy.
FAQ
Q. Does the Extracting Method of Exosomes (such as ultracentrifugation, immunoaffinity capture or commercial kits) Affect the Quantitative Results of Cytokines?
The extracting method of exosomes does affect the quantitative results of cytokines.
Ultracentrifugation: It is a classic method for isolating exosomes, but it may cause aggregation or partial rupture of exosomes, resulting in the loss of some cytokines or co-precipitation of impurities, affecting accuracy.
Immunoaffinity capture: It has high specificity and can selectively isolate exosomes expressing specific markers (such as CD63, CD81), thereby obtaining a higher purity and more specific cytokine spectrum, but it may also miss subpopulations with low expression of certain markers.
Commercial kits: The operation is fast and convenient, but sometimes non-specific impurities such as polymer precipitation will appear, resulting in increased background and may affect the detection of low-abundance cytokines.
Therefore, the choice of specific methods should be reasonably evaluated and optimized based on the research purpose and analytical accuracy requirements.
Q. How to Ensure High-sensitivity Quantitative Analysis When the Concentration of Cytokines in Exosomes is Low?
To address the issue of low cytokine concentrations in exosomes, the following strategies are recommended:
1. Exosome concentration: When extracting exosomes, add a concentration step, such as ultrafiltration or magnetic bead enrichment, to enrich exosomes and the cytokines they carry, improving the sensitivity of analysis.
2. Selection of highly sensitive detection technology: Using highly sensitive methods such as Luminex multiplex immunoassay, ultrasensitive ELISA or high-resolution mass spectrometry can accurately capture low-abundance cytokines.
3. Signal amplification strategy: Use signal amplification methods such as biotin-streptavidin amplification, signal amplification antibody combination technology or nanoparticle-based labeling methods during detection to ensure reliable detection of low-abundance cytokines.
Combining the above strategies can effectively improve the sensitivity of exosome cytokine analysis and avoid missing low-abundance targets in the analysis.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Total Ion Chromatogram & Quality Control Assessment (project-dependent)
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation (project-dependent)
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
6. Raw Data Files
Case Study
This study isolated exosomes from the supernatant of gastric adenocarcinoma cells and analyzed the expression of the cytokine Galectin-3 in exosomes using western blot and ELISA. The results showed that the level of Galectin-3 in exosomes from gastric adenocarcinoma patients was significantly elevated. Furthermore, this exosomal Galectin-3 promoted peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer by altering the peritoneal microenvironment.
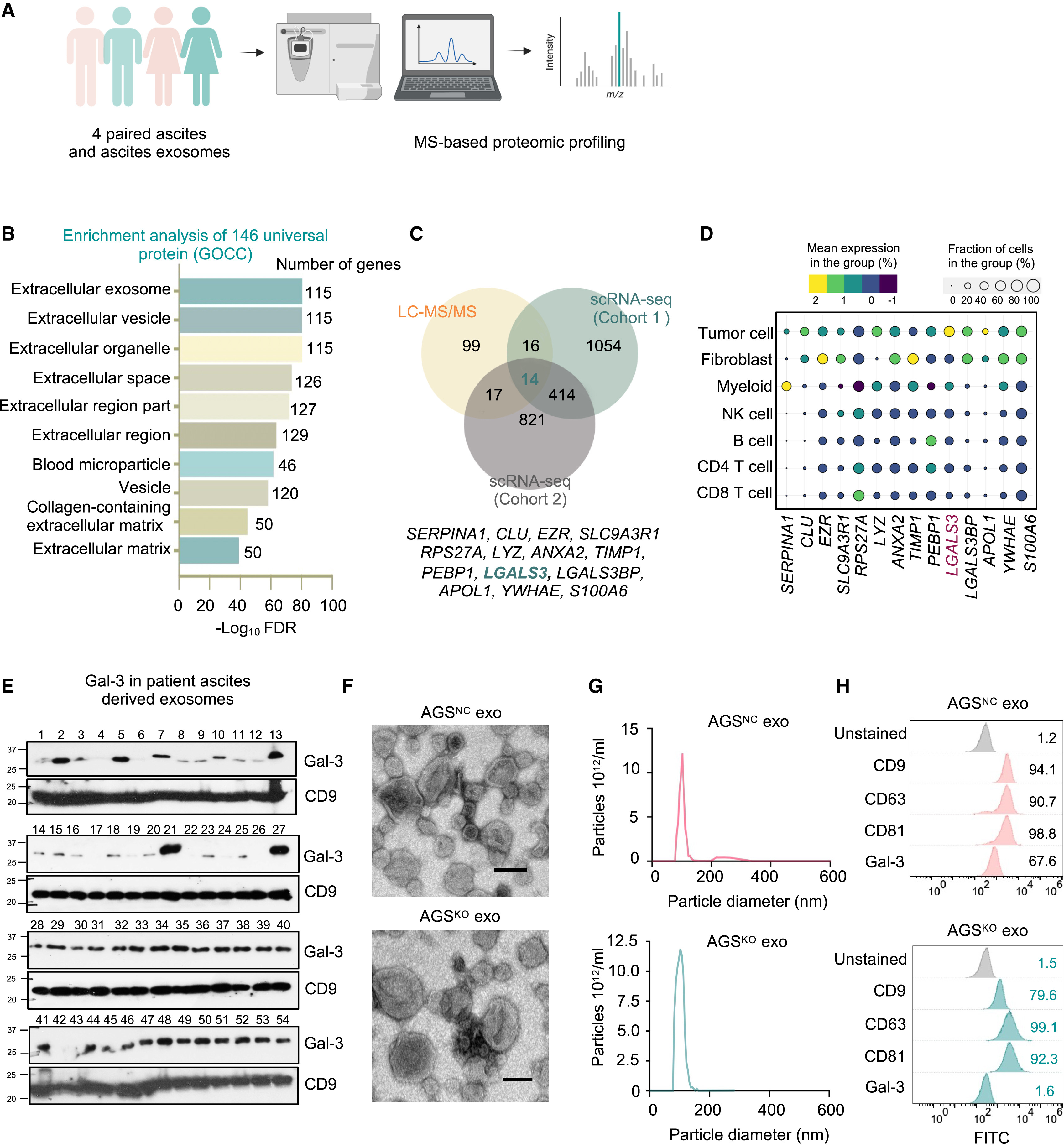
Fan Y. et al. Iscience. 2025.
How to order?







