Edman Degradation Analysis Service
Edman degradation is a classic biochemical method to reveal the N-terminal amino acid sequence of proteins. It is one of the most mature methods in protein N-terminal sequence analysis and has been widely used. MtoZ Biolabs uses Shimadzu's Edman sequencing system to provide N-terminal sequencing services for purified protein products, antibodies, and protein vaccines to scientific researchers and scientific research customers.
Edman degradation was founded and automated by P. Edman in the 1960s. Edman degradation analysis service can be divided into three steps: coupling, cyclization cleavage, and conversion. The specific reaction process: phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC) is coupled to the α-amino group of the N-terminus of the protein under weak base (TMA) conditions. Phenylthiocarboxyl peptide (PTC-AA) is generated, and then under anhydrous strong acid (TFA) conditions, the first residue at the N terminus is removed from the complete polypeptide protein chain as 2-phenylaminothiazolinone (ATZ-AA) is cleaved, and then under dilute acid conditions, ATZ-AA is converted into a more stable phenyl hydantoyl thi N-urea derivative, namely PTH-AA, and the generated PTH-AA is transported to the high-performance liquid phase The amino acid category is identified through analysis in the chromatogram, and which amino acid is determined based on the retention time of the chromatogram. The amide bonds in the remaining peptide chain are not affected and enter the next cycle to continue degradation. Each time a reaction occurs, the amino acid at one position can be identified. When all results are measured, all amino acid sequence results can be obtained. The Edman degradation analysis service by MtoZ Biolabs can determine the sequence information of the N-terminal 30 amino acids.
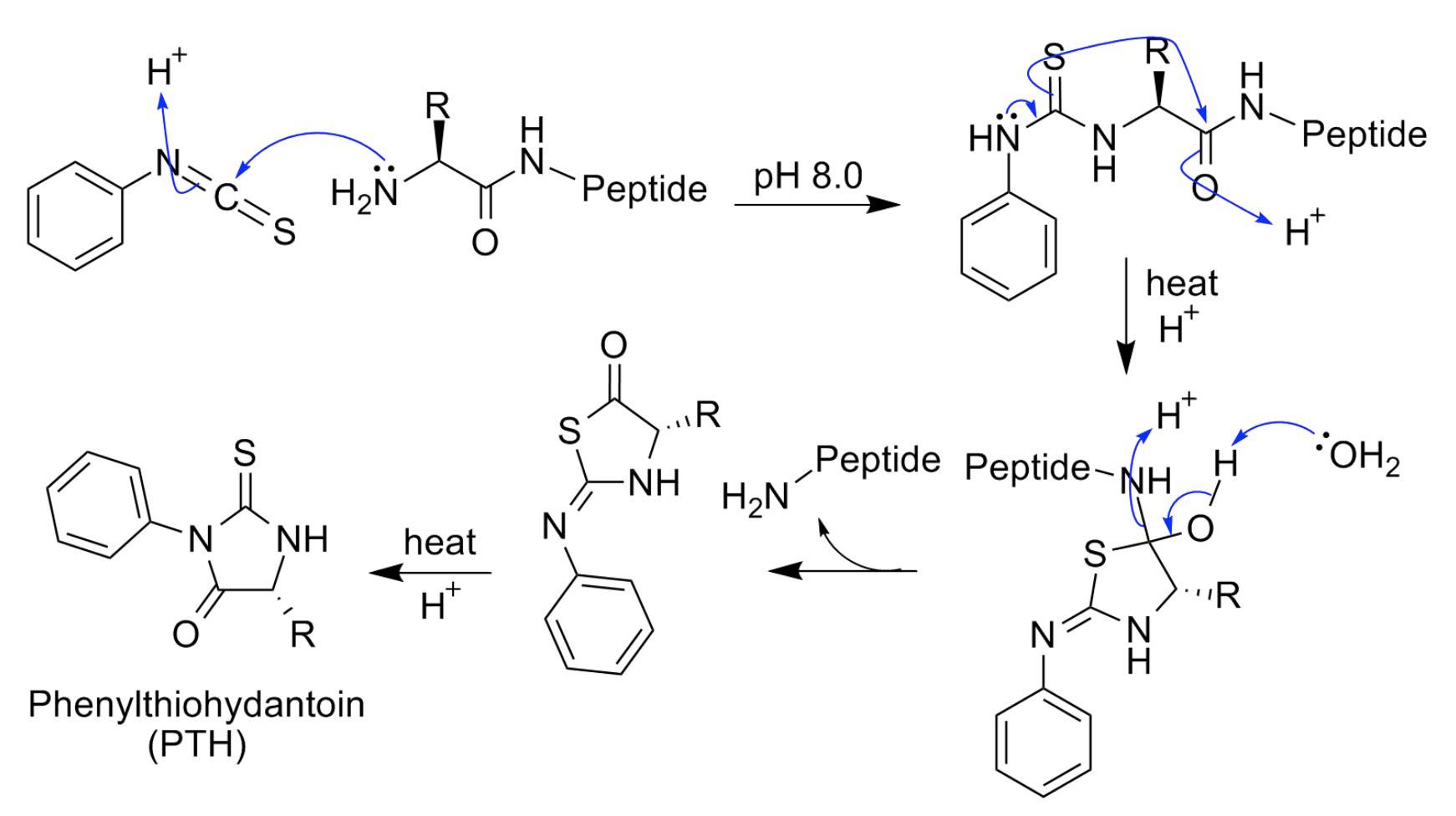
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of Edman degradation principle
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
Using Shimadzu’s sequencing system, MtoZ Biolabs provides Edman degradation analysis service for determining the N-terminal amino acid sequences of purified proteins or peptides with high accuracy and efficiency.
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Analytical Platform
MtoZ Biolabs utilizes Shimadzu’s Edman sequencing system, ensuring reliable, fast, and precise analytical services.
2. Customized Research Solutions
Our Edman degradation analysis service offer tailored solutions based on sample requirements, enabling the analysis of complex mixtures.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Purified Protein or Peptide Samples (Solid/Liquid)
(1) The purity is greater than 90%, and the buffer is water, which can be directly detected; if the product contains a small amount of salt, the buffer can be replaced and detected. Protein samples are usually replaced with ultrafiltration tubes, and peptide samples can be desalted using a C18 membrane.
(2) The purity is less than 90%, the protein bands can be separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membrane. After staining with Ponceau Red or Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250, select the clearly visible target protein bands and use a clean scalpel to remove the target protein bands. Protein bands were excised for Edman sequencing. This method is suitable for protein samples with a molecular weight of about 10-100 kDa. You can complete this step yourself, or we can perform electrophoresis and electrotransfer.
2. PVDF Membrane Protein Samples
Transfer the sample on the protein gel to a PVDF membrane (note: do not use nitrocellulose membranes). After staining with Ponceau Red or Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250, you can prepare 3-6 target bands. If detected the number of amino acids is large, the number of bands should be appropriately increased.
3. Sample Transportation
Pack excised protein bands securely and ship with ice packs.
*Note: For any special requirements or assistance with sample preparation, please contact us.
Applications
1. Validation of Protein Expression Products
Confirm the insertion site and expression sequence of recombinant proteins.
2. Verification of Protein Products in Cell Line Establishment and Fermentation
Verify whether the N-terminal methionine and signal peptide of the protein product are correctly processed during cell line establishment and fermentation.
3. Protein Degradation/Enzymatic Cleavage Analysis
Analyze N-terminal sequences of new protein fragments formed by degradation or enzymatic cleavage to identify cleavage sites.
4. De Novo Sequencing
Analyze novel protein sequences not present in existing protein databases.
Case Study
A recombinant purified protein sample with a theoretical molecular weight of 32.1 kDa (316 amino acids) was stored for one month at 4°C and -20°C, respectively. SDS-PAGE analysis showed that the molecular weight of the -20°C sample matched the theoretical value, whereas the 4°C sample exhibited a lower molecular weight (2-5 kDa less).The two protein samples were sequenced separately using the Edman sequencing system. The results showed that the N-terminal sequence of the -20°C sample protein was consistent with the theoretical sequence, and the N-terminal sequence of the 4°C sample protein started from the 22nd amino acid of the theoretical sequence. It proves that the sample is degraded after being stored at 4°C for one month, which provides effective basis for subsequent research on recombinant expression and purified protein technology, as well as sample storage temperature and cycle.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Chromatograms and Quality Control Assessment(project-dependent)
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation(project-dependent)
5. Raw Data Files
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







