Cerebrospinal Fluid Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis Service
- 1H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR)
- Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
- Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
- Direct Flow Ionization Mass Spectrometry (DFI-MS/MS)
- Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
-
High Sensitivity Detection: Accurately identifies low-abundance metabolites and trace metals, facilitating early diagnosis of neurological diseases.
-
Integrated Technologies: Combines NMR, LC-MS, GC-MS, and other techniques to provide comprehensive CSF metabolomics analysis.
-
Efficient and Cost-Effective Services: Rapid delivery of high-quality results at competitive prices, enhancing research efficiency.
-
Customized Solutions and Expert Support: Offers personalized analysis based on client needs, ensuring successful research outcomes and client satisfaction.
- Brain injury research
- Monitoring of multiple sclerosis
- Early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is secreted within the central nervous system (CNS) and occupies the ventricles, the subarachnoid space of the brain, and the spinal column. CSF serves to protect the brain from physical impacts and plays a vital role in nutrient and chemical circulation in the blood, as well as in waste management. This involves the active transport and facilitation of bulk flow from the extracellular fluid of the brain to the subarachnoid space, eventually reaching the venous and lymphatic systems, alongside the removal of organic acids. Human CSF is recognized for its abundance of small molecule biomarkers relevant to neurodegenerative and neurological diseases. Despite challenges in obtaining CSF, its relatively straightforward metabolism and significance in CNS diseases underscore its importance in biomedical research and clinical chemistry. High-throughput metabolomic technologies for CSF analysis include:
CSF is rich in trace metals, and ICP-MS is particularly effective for the quantitative analysis of trace metals in biological samples, allowing for the identification and quantification of multiple trace metals. The DFI-MS/MS method enables the quantitative analysis of various compounds that may not be detectable by GC-MS, LC-MS, or NMR techniques.
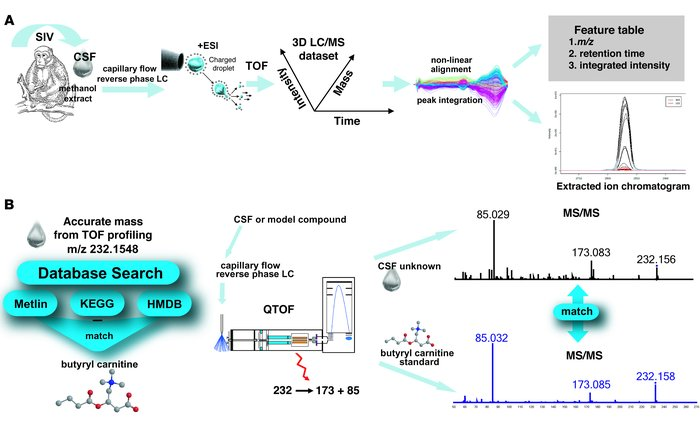
Wikoff, WR. et al. J Clin Invest. 2008.
Figure 1. CSF Untargeted Metabolomics
Service Advantages
Sample Submission Requirements
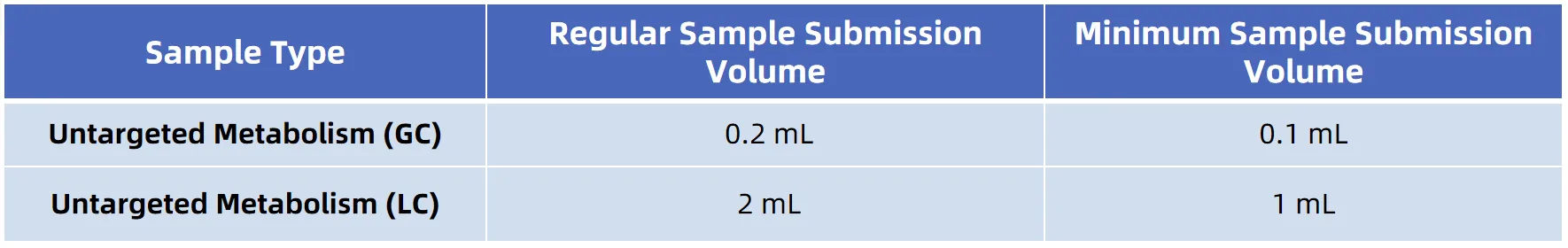
CSF samples should be stored in a freezer at -80°C. Due to the instability of CSF metabolites, repeated freeze-thaw cycles and higher storage temperatures (such as 4°C) should be avoided.
Applications
CSF untargeted metabolomics analysis has applications in:
How to order?







