Chemical Proteomics Service
Chemical proteomics is an emerging interdisciplinary field that integrates techniques and concepts from chemistry, biology, and proteomics to investigate the interactions between small molecules and proteins. At its core, chemical proteomics leverages chemical tools and methodologies to identify and analyze proteins, elucidating their functions and regulatory mechanisms. Scientists leverage chemical proteomics service to gain a deeper understanding of the role of proteins in the onset and progression of diseases, offering new perspectives for drug development and disease treatment.
The application of chemical proteomics is particularly impactful in disease research. It enables scientists to identify disease-associated biomarkers, uncover the molecular mechanisms underlying disease onset, and discover potential drug targets. For example, activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) allows researchers to screen enzyme proteins linked to specific diseases, studying their activity changes and functions. Additionally, compound-centric chemical proteomics (CCCP) facilitates the exploration of interactions between small molecule compounds and proteins, which is critical for drug screening and mechanism studies.
Advancements in chemical proteomics technologies, such as MS-based thermal stability profiling and non-canonical amino acid labeling, provide innovative tools for studying protein thermal stability and dynamic changes. As these technologies evolve, chemical proteomics service is becoming increasingly significant in precision medicine and personalized treatment. They not only enhance our understanding of disease mechanisms but also guide the development of novel drugs and the repurposing of existing therapies, offering patients more effective treatment options.
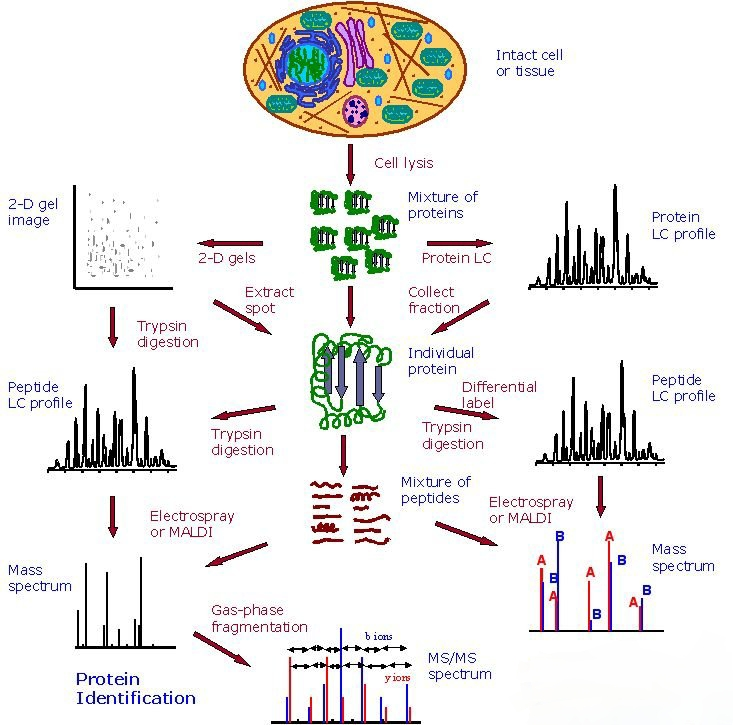
Figure 1. Applications of Chemical Proteomics in Drug Discovery and Development.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Leveraging high-resolution mass spectrometry instruments, MtoZ Biolabs provides comprehensive chemical proteomics service for biomarker research, drug and target discovery, pathway modeling, and mechanism of action studies. Our goal is to deliver high-quality, all-encompassing target deconvolution solutions tailored to meet diverse client needs. We offer various approaches to identify and validate novel drug targets, with our services focusing on the following two core technical areas:
1. Probe Design and Synthesis
Probe design and synthesis in chemical proteomics service is the initial and critical step in target identification. MtoZ Biolabs offers the following commonly used probes:
(1) Immobilized Probes: Active natural products are covalently immobilized on biocompatible inert resins (e.g., agarose and magnetic beads) to act as baits for screening target proteins from active proteomes.
(2) Activity-Based Probes (ABPs): ABPs take into account the activity of drug molecules, interacting with proteins in active proteomes prior to enrichment. ABPs can even penetrate cell membranes and bind to target proteins in live cells, reflecting true physiological interactions.
(3) Click Chemistry Probes: These probes undergo bio-orthogonal click reactions with their complements (e.g., azides, alkynes) to covalently attach affinity tags (e.g., biotin-azide, biotin-cyclopropane) or fluorescent labels (e.g., rhodamine-azide, FITC-azide) for subsequent enrichment and target identification.
(4) Photoaffinity Probes: These probes combine a click chemistry backbone with a photoaffinity group that covalently binds the probe to its target under specific wavelengths of light, forming stable complexes for target identification.
2. Label-Free Chemical Proteomics Methods
For natural products lacking suitable modification sites or whose activity is affected by modifications, MtoZ Biolabs offers label-free chemical proteomics methods based on Drug Affinity Responsive Target Stability (DARTS) and MS-based thermal stability profiling. DARTS relies on the proteolytic protection conferred to target proteins through interactions with small molecules. The process begins by treating equal aliquots of cell lysates with the target compound, a vehicle control, or inactive analogs. The proteins in the lysates are then subjected to selective proteolysis using proteases. Subsequently, the samples are separated by SDS-PAGE and stained to identify protein bands protected from proteolysis by small molecules. Finally, mass spectrometry (MS) is used to identify the proteins present in each band.
The chemical proteomics service provided by MtoZ Biolabs provide you with comprehensive solutions including the entire process from experimental design, sample preparation, probe synthesis, target identification and data analysis. We provide a one-stop, worry-free service to meet your diverse needs in biomarker research, drug and target discovery, pathway modeling, and mechanism of action studies within the fields of drug development and discovery. With our integrated solutions, you can avoid wasting time and resources on ineffective drug candidates and enhance the success rate of your drug development and discovery plans.
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Analytical Platform
MtoZ Biolabs has established advanced chemical proteomics service platform, delivering reliable, fast, and high-precision analysis.
2. Transparent Pricing
Our pricing structure is transparent, with no hidden fees or additional fees.
3. High Data Quality
Comprehensive data coverage with stringent quality control. Our AI-driven bioinformatics platform integrates all chemical proteomics data to deliver detailed reports.
4. Customizable Research Solutions
MtoZ Biolabs offers personalized services to address unique research challenges and experimental needs.
Applications
1. Drug Discovery and Development
Chemical proteomics service provides a platform for drug discovery by simultaneously analyzing the drug accessibility of thousands of protein targets in cell lysates or even in live cells.
2. Target Discovery for Phenotypic Drug Screening
Chemical proteomics supports target discovery for phenotypic drug screening, enabling researchers to understand the selectivity of compound targets and avoid potential off-target side effects.
3. Development of Protein Degradation Drugs
Chemical proteomics offers new research tools for developing protein degradation drugs, including the discovery of new E3 ligands and related targets.
4. Disease Classification and Subtype Reassessment
Using proteomic features to cluster 660 diseases enables the reassessment of disease classifications and subtypes, offering insights into refined disease categorization.
5. Disease Prediction and Diagnosis
Protein-based models achieve an AUC (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve) value exceeding 0.80 in 183 diseases, aiding in improving early disease diagnosis rates.
6. Drug Target Identification
Chemical proteomics integrates cell biology, synthetic chemistry, and biomolecular mass spectrometry, providing a novel platform for drug target screening and identification.
7. Clinical Functional Proteomics Analysis
Chemical proteomics technology is applied in clinical functional proteomics analysis to unravel functional proteomic characteristics of tumor samples. It reveals functional interactions between secreted ligands and receptor membrane proteins in cancer and stromal cells, contributing valuable data for precision diagnostics, molecular subtyping, and targeted therapeutic strategies.
Case Study
1. Chemical Proteomics Methods for Protein Post-Translational Modifications (PTMs)
The central dogma states that genetic information stored in the double helix structure of DNA guides the precise biosynthesis of RNA and proteins through transcription and translation. Theoretically, the maximum number of protein species in a cell is equal to the number of open reading frames in the genome. However, in reality, protein post-translational modifications (PTMs) greatly expand the diversity and functionality of the proteome (Figure 2). Commonly used chemical proteomics strategies are divided into three categories (Figure 3), all of which are based on the design and development of new chemical probes and aim to better understand the function of protein PTMs. This case discusses the importance of protein post-translational modifications (PTMs) in maintaining the basic structure and function of cells, and the powerful role of chemical proteomics in studying protein PTMs. PTMs can significantly change the surface charge, structure, activation state and interactome of proteins. They are key factors in cell signaling and an important target for disease treatment.
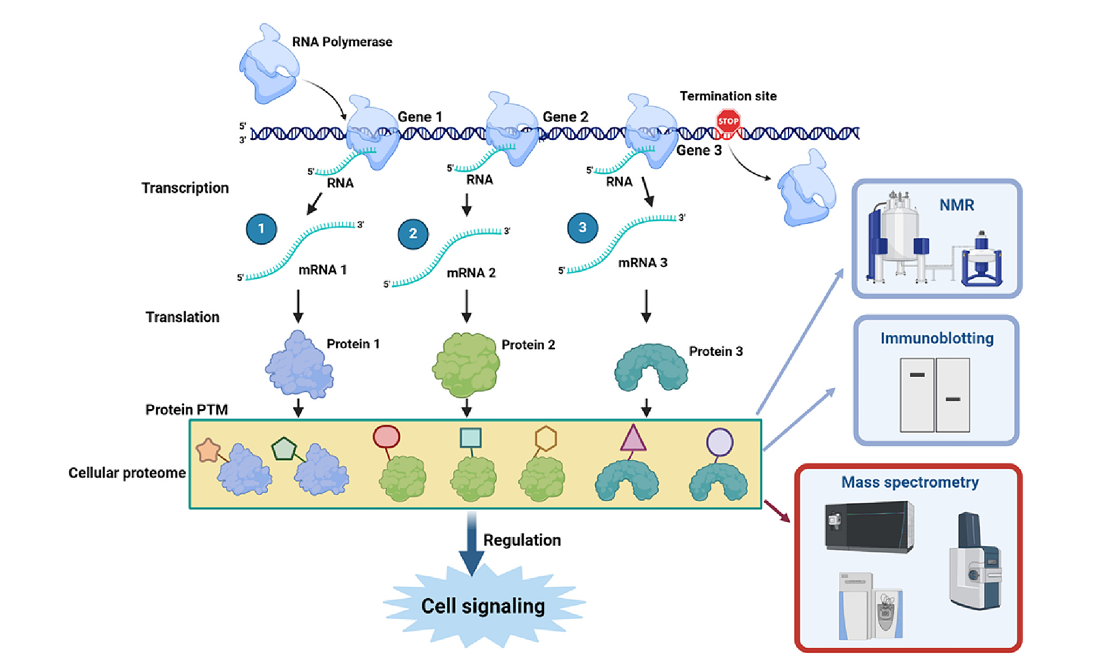
Zhang, N. et al. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom, 2024.
Figure 2. The Complete Flow of the Central Dogma.
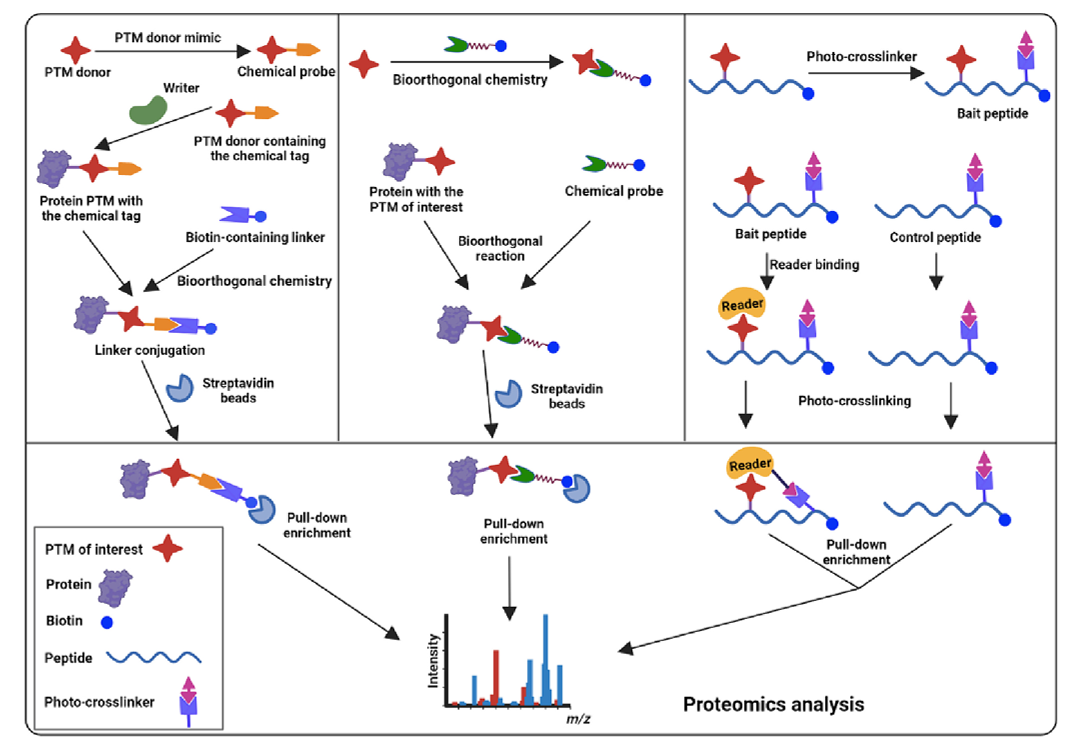
Zhang, N. et al. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom, 2024.
Figure 3. Three Key Chemical Proteomic Methods for Protein PTM Studies.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (MS) Services Provider, provides advanced proteomics, metabolomics, and biopharmaceutical analysis services to researchers in biochemistry, biotechnology, and biopharmaceutical fields. Our ultimate aim is to provide more rapid, high-throughput, and cost-effective analysis, with exceptional data quality and minimal sample consumption. Free project evaluation, welcome to learn more details!
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Biotin Proximity Labeling Service
How to order?







