Cardiolipins Analysis Service
Cardiolipin (CL) consists of two phosphatidyl molecules. It is a tetra-acylated glycerophospholipid that plays crucial roles in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. CL is found in membranes involved in creating electrochemical gradients, which aid in ATP production and substance transporting across the cell membrane. CL is abundant in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells, particularly in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it closely associates with cytochrome c oxidase, necessary for efficient electron transport across cytochrome c oxidase. Furthermore, CL is associated with ATP synthase, the cytochrome bc1 complex, and the ATP/ADP exchange protein F0F1. By facilitating the release of cytochrome c in mitochondria, CL may play a significant role in apoptosis.
CL is composed of four acyl chains, which can be acylated by numerous different acyl chains. This structure results in a vast number of CL molecular species. With more than 10 different kinds of acyl chains randomly distributed among the four esters, there are more than 104 distinct possible CL molecular structures. One type of cell may not contain all these possible CL. The acyl chain composition of CL may vary among different organisms, organs, and cell types. Any alteration in the composition or acylation state of CL can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction. These dysfunctions are associated with various diseases such as aging, as ischemia, hypothyroidism, and heart failure.
Chicco, AJ. et al. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007.
Figure 1. Cardiolipins Analysis
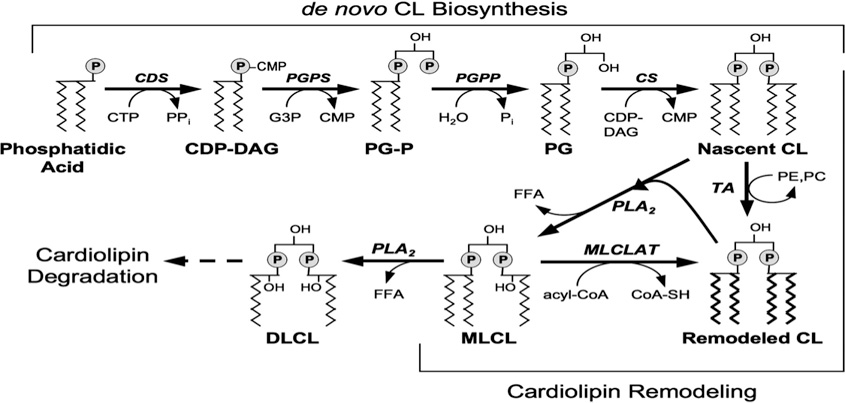
The synthesis pathway of CL is similar to that of other glycerophospholipids. The acylation of glycerol 3-phosphate produces phosphatidic acid, which is then activated to CDP-diacylglycerol (CDP-DAG). CDP-DAG reacts with another glycerol 3-phosphate and produces phosphatidylglycerol phosphate. The phosphatase ia removed from the terminal glycerol by phosphatase and produce phosphatidylglycerol. The biosynthesis pathway of CL converges at this point in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The final steps of CL formation differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In eukaryotes, a second CDP-diacylglycerol molecule reacts with phosphatidylglycerol and CL is produced with CMP released at the same time. In prokaryotes, CL is produced by two phosphatidylglycerol molecules with free glycerol released at the same time.
MtoZ Biolabs provides reliable, fast, and cost-effective cardiolipin analysis services using highly stable, repeatable, and highly sensitive systems for separation, characterization, identification, and quantitative analysis combined with LC-MS/MS.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
1. CL(54:6)
2. CL(68:2)
3.CL(68:3)
4. CL(68:4)
5. CL(68:5)
6. CL(68:6)
7. CL(68:7)
8. CL(70:4)
9. CL(70:5)
10. CL(70:6)
11. CL(70:7)
12. CL(70:8)
13. CL(72:7)
14. CL(72:8)
15. CL(72:9)
16. CL(74:10)
17. CL(74:8)
18. CL(74:9)
19. CL(76:10)
20. CL(76:11)
21. CL(76:12)
22. CL(78:11)
23. CL(78:12)
24. CL(78:13)
25. CL(78:14)
26. CL(80:14)
27. CL(80:15)
28. CL(80:16)
How to order?







