BET Specific Surface Area Testing Service
Specific surface area (SSA) is a critical physical parameter that directly influences a material’s performance in adsorption, catalysis, energy storage, and controlled release applications. Accurate measurement of specific surface area is essential for rational design and quality control of porous solids including catalysts, metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), adsorbents, nanomaterials, polymers, ceramics, and drug delivery systems. MtoZ Biolabs offers a high-precision BET Specific Surface Area Testing Service that enables accurate measurement of specific surface area and supports comprehensive pore structure analysis when combined with complementary techniques such as BJH or DFT.
Technical Principles
BET specific surface area testing based on the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) theory is the most widely accepted and rigorously validated method for quantifying the surface area of solid materials. It relies on measuring the amount of an inert gas—typically nitrogen—adsorbed onto the surface of a sample under controlled conditions at liquid nitrogen temperature (77 K). During analysis, nitrogen gas is introduced in incremental amounts to the sample chamber. As the relative pressure increases, gas molecules begin to adsorb onto the surface through weak van der Waals forces, initially forming a monolayer and subsequently accumulating in multiple layers. By monitoring the volume of gas adsorbed at different pressures, an adsorption isotherm is constructed, which reflects the interaction between the gas molecules and the surface of the solid. The BET theory interprets this isotherm to estimate the amount of gas needed to form a complete monolayer. From this value and the known molecular dimensions of nitrogen, the total accessible surface area of the material can be calculated. This surface area includes both the external surface and the inner surfaces of pores, making the method highly suitable for analyzing porous or finely divided materials. BET analysis is particularly effective for materials with mesopores and micropores, and when combined with complementary models such as BJH (Barrett–Joyner–Halenda), it enables extended pore structure characterization, including pore size distribution and total pore volume.
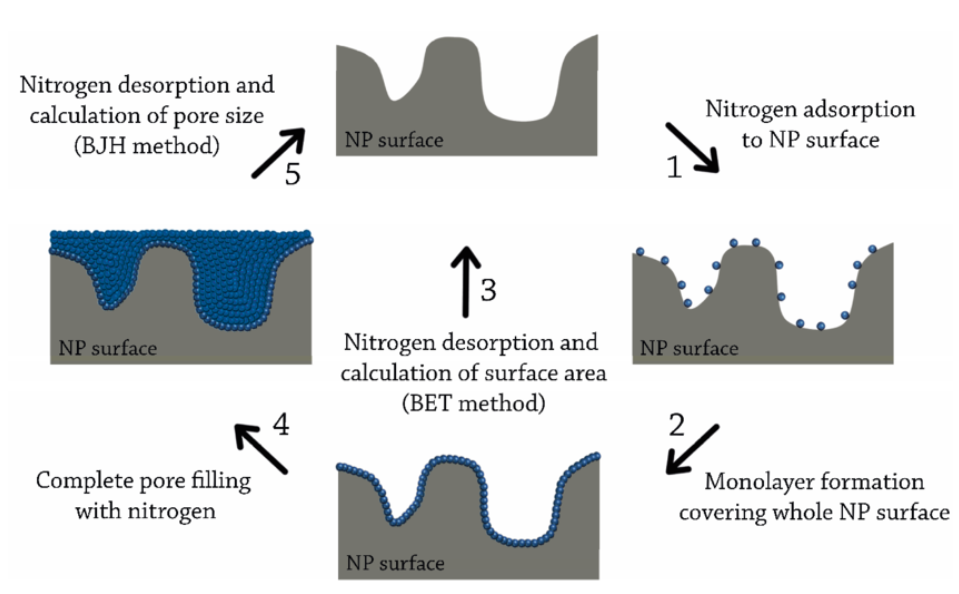
Figure 1. Principles of the BET and BJH Methods
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs employs a range of high-performance instruments with high sensitivity and stability to deliver accurate and reproducible BET specific surface area analysis. Our BET Specific Surface Area Testing Service supports comprehensive characterization of mesoporous, microporous, and total pore structures, including specific surface area, total pore volume, and pore size distribution. We provide tailored degassing protocols, full adsorption–desorption isotherms, and data interpretation using BET and BJH models. This enables researchers and industry clients to evaluate material performance in adsorption, catalysis, and controlled release systems, supporting decisions in product development, quality control, and fundamental research.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Samples are degassed under vacuum or inert gas to remove moisture and contaminants, with conditions adjusted to avoid structural changes.
2. Adsorption-Desorption Measurement
Following preparation, the sample is subjected to nitrogen gas at various relative pressures using high-precision sorption analyzers. This process generates a full adsorption-desorption isotherm, reflecting the amount of gas adsorbed at each pressure point.
3. BET Plot Construction
BET theory is applied to isotherm data to generate a linear BET plot and calculate the monolayer adsorption volume.
4. Specific Surface Area and Porosity Calculation
The BET specific surface area is calculated from the monolayer volume derived from the BET plot. Additional methods such as BJH are applied when required to assess pore size distribution and total pore volume for materials.
5. Reporting and Quality Control
A detailed report is provided with BET specific surface area, pore data, isotherm plots, and other relevant information. Results are reviewed to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Service Advantages
1. Efficient and Fast Turnaround
Streamlined workflows enable rapid sample processing and timely data delivery without compromising analytical rigor.
2. Comprehensive and Flexible
Capable of analyzing mesoporous, microporous, and total pore structures using multiple instrument models to meet diverse research and production needs.
3. Customized Analytical Solutions
Tailored analysis workflows and reporting formats based on sample properties and project objectives.
Applications
BET Specific Surface Area Testing is widely used across various research and industrial domains, including:
💠Pharmaceutical Development: Characterizing drug carriers, excipients, and solid dispersions to evaluate dissolution performance and drug release kinetics.
💠Catalyst Design and Evaluation: Measuring active surface area of solid catalysts to assess catalytic efficiency and support optimization.
💠Nanomaterials and Porous Solids: Analyzing powders, aerogels, MOFs, and graphene-based materials for adsorption, separation, and energy applications.
💠Environmental and Adsorbent Materials: Evaluating biochar, zeolites, and activated carbons for pollutant removal and gas capture performance.
💠Polymer and Composite Characterization: Investigating the surface and porosity properties of advanced polymers, membranes, and nanocomposites.
Case Study
Surface Area and Porosity Analysis of Antimicrobial Nanocomposites

Figure 2. BET Surface Area Analysis Results: N2-Adsorption–Desorption Isotherm Plots of (a) ZnO (Z); (b) ZnO–SnO2 (SZ); (c) ZnO–CuO (CZ); and (d) ZnO–Ag2O/Ag (AZ). Inset Represents the Pore Size Distribution Results
FAQ
Q1: What types of samples are suitable for BET specific surface area testing?
BET analysis is suitable for powders, granules, pellets, and porous solids including catalysts, activated carbon, polymers, ceramics, and drug carriers. We recommend a minimum sample amount of 2 to 5 g depending on material type.
Q2: How should I prepare my samples before submission?
Samples should be a dry solid, free of solvents or volatiles, and sealed in airtight containers. For any special sample handling requirements, please contact our technical team in advance.
How to order?







