MS Protein Sequencing Service
MS Protein Sequencing (Mass spectrometry protein sequencing) is a protein analysis method based on mass spectrometry technology, aimed at accurately identifying and elucidating the amino acid sequences of proteins. MS Protein Sequencing is one of the common methods for protein sequencing. Compared to the Edman degradation method, mass spectrometry is more sensitive, can cleave peptides more rapidly, and can identify proteins with blocked or modified termini. MS protein sequencing service can determine the full protein sequence, the N-terminal sequence, and the C-terminal sequence of proteins. Utilizing the high-resolution mass spectrometry platform, MtoZ Biolabs provides professional MS protein sequencing service which can achieve 100% coverage of the target protein sequence, to assist you in making breakthrough advances in the field of protein research.
Technical Principles
The fundamental principle of MS protein sequencing involves ionizing proteins or their peptide fragments and analyzing the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of these ions using a mass spectrometer to obtain molecular information, thereby deducing the amino acid sequence of the protein.
MS protein sequencing typically does not analyze the complete protein directly. Instead, the protein is first degraded into smaller peptide fragments through chemical or enzymatic hydrolysis. These peptide fragments are then ionized using techniques such as electrospray ionization (ESI) or matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI). The mass spectrometer separates and detects the peptide fragments based on their m/z, generating a mass spectrum of the peptides. By analyzing and comparing the mass spectrometry data with known protein databases or by deconvoluting the characteristic information of fragment ions, the amino acid sequence of the protein can be accurately determined.
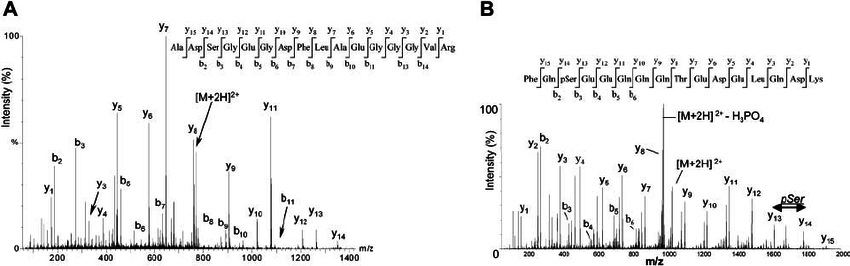
Cristea I M , et al. Blood, 2004.
Analysis Workflow
Protein Extraction and Purification
Depending on the sample type, select an appropriate extraction method such as buffer lysis, ultrasonic disintegration, or chemical extraction for protein extraction. Subsequently, purify the target proteins using techniques such as salting out, gel filtration, or ion exchange chromatography.
Enzymatic Digestion and Peptide Generation
Utilize specific enzymes (e.g., trypsin, chymotrypsin) to digest the proteins, generating peptides with specific end groups.
Peptide Separation and Mass Spectrometry Analysis
To enhance sensitivity and resolution of the analysis, employ techniques like liquid chromatography to first separate the peptides. Following separation, use the high-resolution mass spectrometer to ionize and detect the peptides, thereby obtaining high-quality mass spectrometry data.
Data Processing and Analysis
Identify and match protein sequences based on mass spectrometry data through an advanced software platform. Based on sequence information, the function, structure and role of the protein in biological processes can be further inferred.
Case Study
MS protein sequencing was used to analyze the structural of the new virus protein ZmBWV.
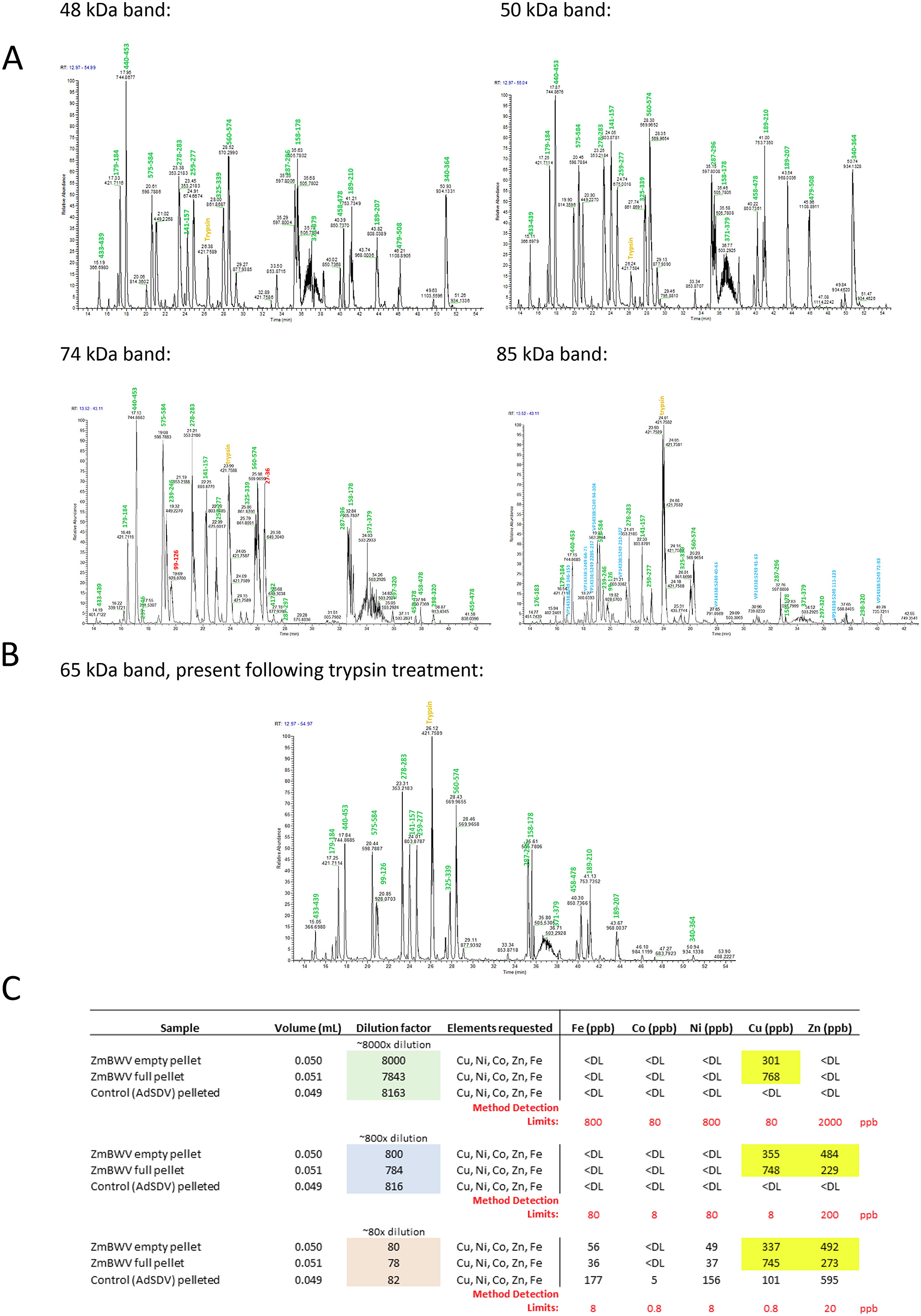
Penzes J J. et al. Cell. 2024
Why Choose MtoZ Biolabs?
1. Advanced Analysis Platform: MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced MS protein sequencing platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
2. One-Time-Charge: Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
3. High-Data-Quality: Deep data coverage with strict data quality control. AI-powered bioinformatics platform integrates all MS protein sequencing data, providing clients with a comprehensive data report.
4. 100% Protein Sequence Determination: In the typical protein sequencing process, only trypsin is used to digest the protein, resulting in an identified peptide coverage of approximately 60%. To obtain the complete sequence information of the target protein, MtoZ Biolabs selects six proteases (Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Asp-N, Glu-C, Lys-C, and Lys-N) to individually digest and perform mass spectrometry analysis on the target protein. By obtaining fragmented peptide segments and subsequently assembling them, MtoZ Biolabs achieves 100% determination of the protein sequence.
Sample Submission Suggestions
Sample Types
We accept samples from a variety of sources, including but not limited to animal and plant tissues, serum, plasma, urine, and high-purity protein samples.
Sample Quantity
We recommend providing 50-100 μg of protein to ensure high-quality sequencing results. You may also contact us for consultation before submitting your samples.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Total Ion Chromatogram & Quality Control Assessment (project-dependent)
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation (project-dependent)
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
6. Raw Data Files
FAQ
Q: How to Optimize Enzymolysis Conditions to Ensure Complete and Specific Enzymatic Cleavage?
The key factors to optimize the enzymolysis conditions are as follows.
Enzyme-to-Substrate Ratio (Amount of Enzyme): In general, the mass ratio of enzyme to protein is between 1:50 and 1:100. Excessive enzyme may lead to non-specific cleavage, while insufficient enzyme may result in incomplete digestion. Gradient experiments (e.g., 1:50, 1:75, 1:100) can be conducted to test the impact of different enzyme amounts on the enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency, thereby selecting the optimal ratio.
Reaction Time: Prolonged reaction times may cause peptide degradation or non-specific cleavage. Sampling and analysis at different time points (such as 4 hours, 8 hours, and 16 hours) can be performed to evaluate the progress and efficiency of digestion, thereby determining the optimal reaction time.
Reaction Temperature: Enzymatic digestion is typically carried out at 37°C, as most proteases exhibit optimal activity at this temperature. If necessary, the temperature can be adjusted based on the specific characteristics of the enzyme.
pH: Select an appropriate buffer and ensure that the pH remains stable during the digestion process, preventing fluctuations in enzyme activity due to pH changes.
Reduction and Alkylation: The concentration and reaction time of reducing agents and alkylating agents need to be optimized based on the sample properties and enzyme characteristics to avoid sample loss due to excessive usage.
Treatment after Enzymatic Hydrolysis: Terminate the enzymatic hydrolysis by adding organic solvents (such as acetonitrile), acids (such as TFA), or by heating, to prevent further enzyme activity. Solid-phase extraction or other methods can be used to remove unreacted enzymes, avoiding interference with subsequent mass spectrometry analysis.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Protein Sequence Analysis Service
How to order?







